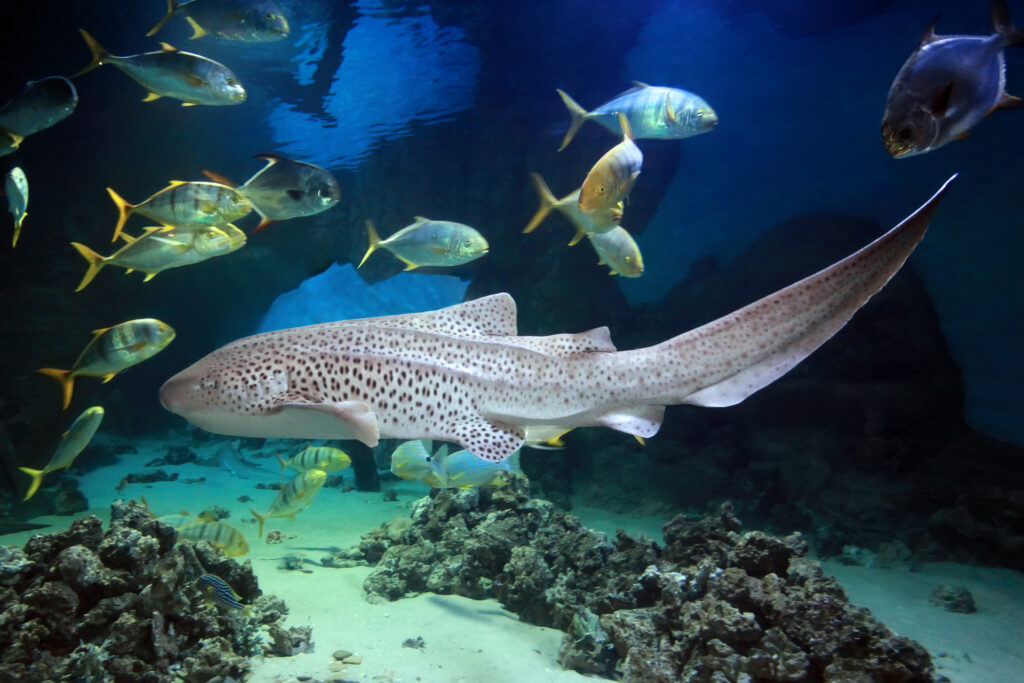
Zebra shark
Stegostoma fasciatum
MAXIMUM LENGTH
314 cm
FEEDING
Carnivore
ACTIVITY

Nocturnal
Adults are yellow-brown with dark brown spots while the young are dark in color with white spots and stripes, fading to a pale ventral surface. The juveniles’ stripes are what give this species its common name of zebra. They live on sand, rock reefs, and coral bottoms, usually sluggish during daylight hours, becoming active to hunt nocturnally. It is often observed sitting on the bottom in close proximity to coral reefs.
These nocturnal hunters feed primarily on mollusks, crustaceans, small bony fishes, and even sea snakes. Sucking their prey up with powerful buccal cavity muscles.
REPRODUCTION
This species is oviparous, releasing egg cases into the environment, which anchor to the bottom substrate with hair-like fibers.
INTERESTING FACTS
Zebra sharks are known to reproduce asexually as well, via parthenogenesis: the development of an unfertilized egg, making the offspring essentially a clone of the mother.
Distribution
Conservation status